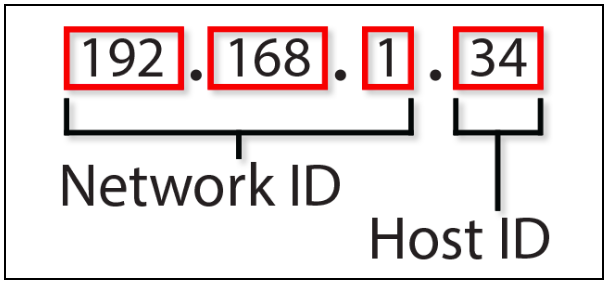
An IP address consists of two parts, the network ID and the host ID. The network ID is the left part of the IP address. It describes the specific network.
In a home network, the IP address could be 192.168.1.34, where the first 7 digits make up the network ID of the address. Usually the missing last part is filled by a zero, so that the network ID of the device is 192.168.1.0.
Example of IP Range & Meaning of Host ID
The host ID is the trailing part of the IP address. It does not identify a network like the network ID, but the hosts. The word “hosts” is commonly used in the IP world for the term device.
In the example it means that the host ID is 34. All devices carry their own host ID. Within the home network, devices can have IP addresses such as 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.30, and 192.168.1.34. The host IDs in this case would be: 1, 2, 30 and 34. Each device is hereby assigned a unique host ID.
The example shows excellently that IP addresses work like street addresses. Imagine that the street name is the network ID and the house number is the host ID. Each street name is unique and therefore exists only once in the city. Likewise, network IDs and host IDs (within the network) are not assigned twice.
Subnets and subnetting
Subnetting divides the network into subnetworks. You borrow bits from the host ID to create a subnet with. Subnets are used to avoid overloading the network. This is especially the case if there are several devices (hosts) within a network.
Several IP addresses are grouped together within a subnet. Data packets are brought directly through the correct network address. As a result, they do not go through different IP addresses until the correct one is reached. Subnets are used when multiple hosts or devices are connected to a large network.
In most homes or small businesses, you will find subnet masks such as 255.255.255.0. The position of the changes from 255 to 0 indicates the separation between the network ID and the host ID. The 255s “mask” the network ID out of the equation.
IPv4 and IPv6
IPv6 was developed in the mid-1990s. The 4 billion IP addresses of IPv4 were no longer sufficient. IPv4 is a shorter form and follows the 32-bit addressing scheme. IPv6 are 128 bits long, which means that significantly more addresses can be formed.
With IPv6, the popular subnet mask is dropped. Not mandatory, but it is simply no longer fundamentally necessary. Network partitioning can be redesigned with IPv6. IPv6 provide the large address space required for this.
Each application can get its own IPv6 address. This makes conversions such as a hardware change easier. The IP of the hardware can be changed without changing the IPv6 address of the application.
How do I find out my IP address?
You can easily find out your own IP yourself.
- Use the right mouse button on your Windows logo and go to “Network Connections.”
- Click “View Network Properties.”
- Behind the information IPv4 address or IPv6 address you will find your IP address.
Anonymity and data protection
The European Court of Justice (ECJ) has ruled that static and dynamic IP addresses are considered personal data in terms of data protection. They are therefore particularly worthy of protection! A website operator may only store the IP address if this is necessary for the use of the website. For example, an online retailer uses various web analytics tools for market research purposes and stores the IP address. Here, explicit consent must be obtained via a checkbox in the order process.
FAQ
To help you get an overview, we have listed the most important questions for this article: